Contents
- 1 Refrigeration System Problem and Solution:
- 2 Cold storage facility Not Cooling
- 3 Fixing High Compressor Suction Pressure
- 4 Fixing Low Compressor Suction Pressure
- 5 What Causes High Compressor Discharge Pressure?
- 6 Refrigeration System Making Abnormal Noise? What to Do
- 7 Compressor low oil pressure
- 8 How to know if a refrigeration system on low lube oil pressure:
- 9 Troubleshooting Excess Compressor Overload?
- 10 How to Identify and Fix Low and High Refrigerant Charges
- 11 Troubleshooting Moisture in the Refrigeration System
- 12 How to Prevent Short Cycling in a Refrigeration Compressor
- 13 What is compressor anti-recycling?
- 14 How to Identify and Fix Frosting at the Suction of the Compressor
- 15 Troubleshooting Air In Refrigeration System and how to remove it?
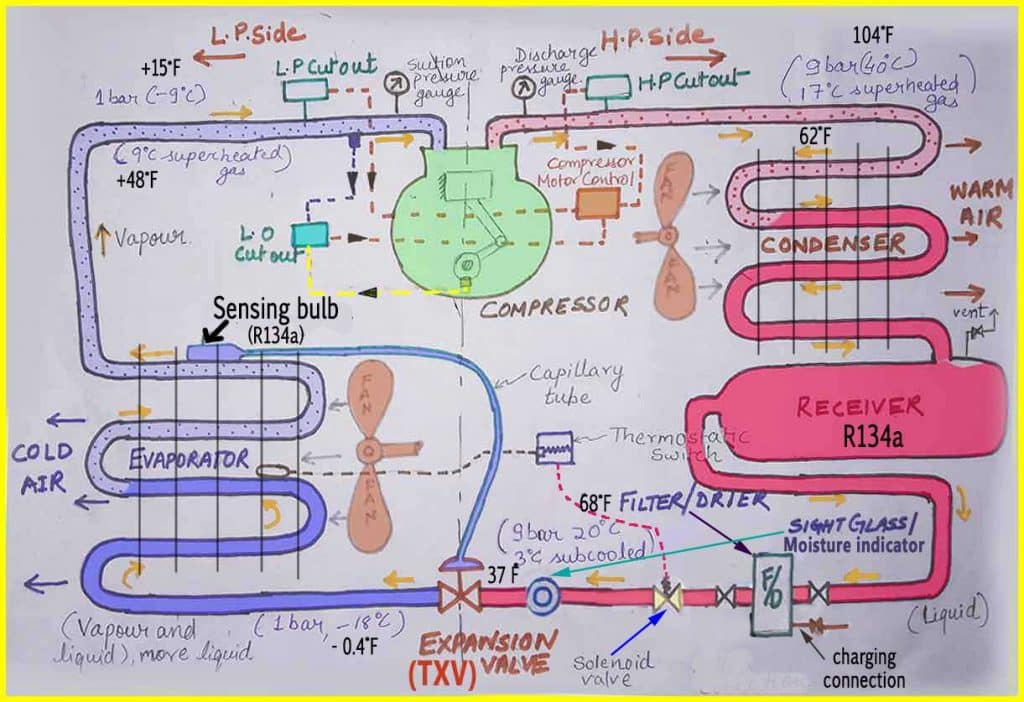
Refrigeration System Problem and Solution:
Cold storage facility Not Cooling
- Lack of refrigerant present in the system.
- Blocked filter at the drier or expansion valve.
- Evaporator inlet solenoid closed.
- Condenser fan motor issue, less heat transfer available for a given mass of refrigerant.
- Defrosting element still operational.
- Compressor capacity control faulty leading to less coolant across the thermostatic expansion valve.
Fixing High Compressor Suction Pressure
- Fractured compressor valves, causing the compressor capacity to fall.
- Evaporator load too high, caused by room items recently changed entry door left open.
- Excess refrigerant charge. This fault is combined with a low compressor superheat and indicates liquid in the suction line. The solenoid valve should be closed quickly to prevent liquid damage to the compressor.
- Expansion valve stuck in a fully open position, caused by dirt in the expansion valve.
Fixing Low Compressor Suction Pressure
- Blocked filter or closed valve in the system. In this mode, the compressor is extracting more from the evaporator than the expansion valve is supplying leading to low suction pressure and possibly compressor to short cycle.
- Refrigerant charge too low. There is not enough refrigerant within the system to allow the compressor to operate at the present capacity setting. Increased compressor run time.
- The liquid refrigerant flow may be disturbed: Fully open the valves in the liquid refrigerant line if not fully open. Confirm line filters not chocked.
- Thermostatic expansion valve clogged with ice or oil dust mixture: Dissemble expansion valve (TEV) and clean the ice with dry compressed air. Activate the desiccant of drier filter by the heater. Take off oil mixture dirt.
- Less opening for the expansion valve or superheat very low: Adjust the expansion valve opening and ensure temperature sensor attached properly to the evaporator outlet.
- Evaporator cooling capacity lowered by dust and frost: Check fan operation working normal. Remove dust by soft brush and carry out defrosting
What Causes High Compressor Discharge Pressure?
- This condition causes the compressor to overload the prime mover, and expose the high-pressure side of the system to overpressure
- The system overpressure avoided by fitting a compressor motor trip and relief valve at the compressor outlet
Causes for discharge high pressure:
- Low coolant or air flow to the condenser. The temperature of the condensing refrigerant gas rises as the coolant or ambient air temperature rises. This cause the condensing pressure to rise and a high-pressure trip.
- Air in the refrigeration system prevents the condenser to operate at its full capacity and partly insulate the condenser. This symptom would cause the superheat temperature of the compressor outlet to rise.
- Condenser outlet valve closed, causing liquid level in the condenser to rise and producing a similar fault as above.
Refrigeration System Making Abnormal Noise? What to Do
- Anchor bolts or clamp bolts loosened. Tighten up anchor and clamp bolts.
- The liquid is going to the compressor suction line. Adjust the expansion valve and check temperature sensor adhered firmly to the evaporator
- Foamed oil compressed. Adjust the quantity of oil in the compressor crankcase.
- Suction valve plate, the delivery valve plate, piston pin, bearing, connecting-rod are damaged or worn. Check for noise location and repair it.
- Refrigerant intel valve throttled and refrigerant velocity high, causing vibration in valve plates. Fully open refrigerant inlet valve.
Compressor low oil pressure
- With the screw compressor unit, the oil is continually removed from the oil separator by either the electrically driven lube oil pump or by a shaft driven lube oil pump.
- The suction pressure of the oil gear pump is the compressor discharge pressure, hence the delivery pressure of the oil pump must be greater than this, to inject the oil into the bearing and sliding parts.
- Low lube oil pressure operates a compressor motor trip switch; otherwise, rapid rotor overloading would occur.
How to know if a refrigeration system on low lube oil pressure:
Chocked oil filter
- The oil pressure gauge indicates the pressure drop across the filter.
- Clean the filter thoroughly and renew the crankcase oil when the time comes and check for tiny metal parts or debris after draining the oil from the crankcase.
Oil separator blockage preventing oil return to the compressor
- Oil separator works on a cyclonic basis, ie. By causing the oil to impinge on the separator wall, coalesce, and drain to the separator bottom.
- There could be a blockage of oil separator outlet line by material discharges by the compressor. The level indicator in the separator unit should indicate this cause.
Troubleshooting Oil Carryover in Refrigeration Systems
- When the compressor is operating on low loads, the efficiency of the oil separator falls, and the refrigerant gas speed also falls.
- This allows oil to discharge from the system, and it gets collected in the areas where gas speeds are low, usually within the evaporator area.
Bearing wear within the compressor.
- Bearing wear allows a high leakage from the clearances, causing the oil pressure to fall. Bearing wear leads to premature crankshaft wear.
Troubleshooting Excess Compressor Overload?
This fault can cause the compressor to trip.
Possible cause includes:
- Excess evaporator load which can occur when the room is warm and the compressor is allowed to go to full load.
- Compressor crankshaft seizure due to faulty lubrication.
How to Identify and Fix Low and High Refrigerant Charges
Undercharge symptoms:
- Low discharge and suction pressure.
- Compressor motor getting tripped by low pressure cut out trip.
- Large bubbles in the liquid sight glass.
- Compressor discharge temperature high.
- The compressor runs longer period between the start and stop.
Solution:
- Charge the system until the bubbles disappear.
- Achieve the correct pressure gauge reading.
- Check for leaky points by halide torch or soap solution or electronic leak detectors.
Overcharge symptoms:
Refrigerating plants should not be charged with excess refrigerant, as this may overload or damage the compressor. To ensure refrigerant charged correctly, weigh the refrigerant before charging.
Symptoms are:
- High compressor discharge pressure.
- Full level clear sight glass.
- The compressor is running cold.
- Excess frost on the compressor suction.
- Unusually large compressor noise while running due to liquid refrigerant entering into the compressor suction.
Solution:
- Release the refrigerant into a recovery bottle and avoid any leaks directly into the atmosphere.
Troubleshooting Moisture in the Refrigeration System
Evaporator starving of refrigerant and rapid rise in condenser pressure causes a compressor to short cycle.
Icing at the expansion valve filter.
In case of a hermetic compressor, moisture can cause corrosion and damage to the motor windings.
Remedy:
- Clean expansion valve filter.
- Renew filter drier unit.
How to Prevent Short Cycling in a Refrigeration Compressor
Short cycling means the compressor is repeatedly running for a few seconds and then cutting off.
Reasons for above:
- Refrigerant charge is too low.
- Low pressure cut out is not properly adjusted.
- Frosting or clogging of the evaporator.
- Filter / Drier chocked.
- Moisture in the system.
- Compressor unloader mechanism is not working properly.
- Expansion valve not adjusted correctly leading to excess superheat.
- Liquid line solenoid valve malfunctioning.
What is compressor anti-recycling?
It is the time delay before the compressor motor starts again, basically to protect the motor from frequent starts which is also known as “short cycling.”
How to Identify and Fix Frosting at the Suction of the Compressor
It means the liquid is reaching suction of the compressor and is absorbing heat from the surroundings resulting in ice formation.
Reasons:
- Thermostatic expansion valve stuck in open position.
- Superheat setting is low and not proper.
- The thermostatic bulb not touching the evaporator outlet pipe, or capillary tube damaged.
- Refrigerant overcharged.
- Fan tripped or damaged.
- Liquid entering inside the crankcase boils off taking away heat from lube oil which may cause foaming.
Troubleshooting Air In Refrigeration System and how to remove it?
Indication for air ingress
- Compressor overheating with high discharge pressure and normal condensing temperature.
- The appearance of small bubbles in the sight glass.
- Condensing pressure high.
- Cooling capacity reduced.
- Pressure gauge of the condenser jumps indefinitely.
Reason:
- Air may enter while charging of the refrigerant.
- Air may enter while carrying out routine maintenance.
- If the suction pressure goes below atmospheric pressure, during system evacuation, then air may enter from leaky gaskets or loose connections.
Remedy:
- Air in the system gets removed by collecting the system gas into the condenser by closing the condenser outlet valve while the compressor is running.
- The compressor trips after the activation of low pressure cut out with most of the refrigerant collected inside the condenser.
- Allow the condenser to cool down with a fan or cooling water whichever is the medium under running condition.
- As the air is non-condensable, it remains on top of the condenser above the refrigerant.
- Vent the collected air from the venting valve using a thermometer, as the temperature drops, immediately shut the vent valve.


What causes high pressure failure?
An overcharge of liquid refrigerant can cause high-pressure failure, may lead to damage in moving parts of the compressor.